

Although Horner's syndrome can occur in adults it usually occurs in infants as a result of a birth injury. doi: 10.1097/'s syndrome is an uncommon health condition in which nerve damage disrupts the brain's control over the eye. Straight hair and congenital horner syndrome. Wang FM, Wertenbaker C, Cho H, Marmor MA, Ahn-Lee SS, Bernard BA.
Unequal pupil size in infants free#
Citation on PubMed or Free article on PubMed Central
Syndrome and the risk of neuroblastoma: a population-based study. Smith SJ, Diehl N, Leavitt JA, Mohney BG.Heterochromia Iridis in congenital Horner's Neuroblastoma and other responsible mass lesions. Horner syndrome: etiologies and roles of imaging and urine studies to detect Mahoney NR, Liu GT, Menacker SJ, Wilson MC, Hogarty MD, Maris JM.

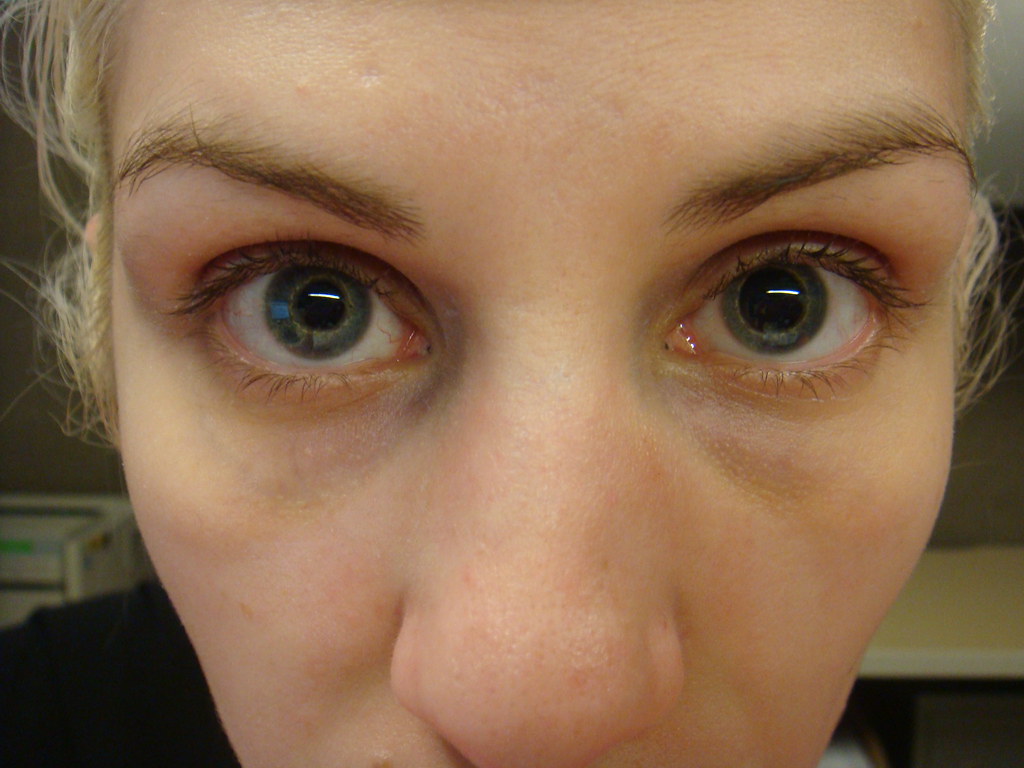
 Jeffery AR, Ellis FJ, Repka MX, Buncic JR. Fons C, Vasconcelos M, Vidal M, Puy R, Capdevila A, Sanchez L, Campistol J.Īgenesis of internal carotid artery in a child with ipsilateral Horner's. These cases are referred to as idiopathic Horner syndrome. Some people with Horner syndrome have neither a known problem that would lead to nerve damage nor any history of the disorder in their family. When the headache is gone, the signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome usually also go away. The signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome can also occur during a migraine headache. Tearing of the layers of the carotid artery wall (carotid artery dissection) can also lead to Horner syndrome. Some individuals with congenital Horner syndrome have a lack of development (agenesis) of the carotid artery. Horner syndrome can also be caused by problems with the artery that supplies blood to the head and neck (the carotid artery ) on the affected side, resulting in loss of blood flow to the nerves. The nerves related to Horner syndrome can also be damaged by a benign or cancerous tumor, for example a childhood cancer of the nerve tissues called a neuroblastoma. Horner syndrome that occurs very early in life can lead to iris heterochromia because the development of the pigmentation (coloring) of the iris is under the control of the cervical sympathetic nerves.ĭamage to the cervical sympathetic nerves can be caused by a direct injury to the nerves themselves, which can result from trauma that might occur during a difficult birth, surgery, or accidental injury. Problems with the function of these nerves cause the signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome. The cervical sympathetic nerves control several functions in the eye and face such as dilation of the pupil and sweating. Within the autonomic nervous system, the nerves are part of a subdivision called the sympathetic nervous system. These nerves belong to the part of the nervous system that controls involuntary functions (the autonomic nervous system). Horner syndrome that appears after the newborn period (acquired Horner syndrome) and most cases of congenital Horner syndrome result from damage to nerves called the cervical sympathetics. However, the nerve damage that causes Horner syndrome may result from other health problems, some of which can be life-threatening.Īlthough congenital Horner syndrome can be passed down in families, no associated genes have been identified. The abnormalities in the eye area related to Horner syndrome do not generally affect vision or health. Individuals who develop Horner syndrome after age 2 do not generally have iris heterochromia. In people with Horner syndrome that occurs before the age of 2, the colored part (iris) of the eyes may differ in color (iris heterochromia), with the iris of the affected eye being lighter in color than that of the unaffected eye. Sinking of the eye into its cavity (enophthalmos) and a bloodshot eye often occur in this disorder. Horner syndrome is characterized by drooping of the upper eyelid ( ptosis ) on the affected side, a constricted pupil in the affected eye (miosis) resulting in unequal pupil size (anisocoria), and absent sweating (anhidrosis) on the affected side of the face. Horner syndrome can appear at any time of life in about 5 percent of affected individuals, the disorder is present from birth (congenital). Horner syndrome is a disorder that affects the eye and surrounding tissues on one side of the face and results from paralysis of certain nerves.
Jeffery AR, Ellis FJ, Repka MX, Buncic JR. Fons C, Vasconcelos M, Vidal M, Puy R, Capdevila A, Sanchez L, Campistol J.Īgenesis of internal carotid artery in a child with ipsilateral Horner's. These cases are referred to as idiopathic Horner syndrome. Some people with Horner syndrome have neither a known problem that would lead to nerve damage nor any history of the disorder in their family. When the headache is gone, the signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome usually also go away. The signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome can also occur during a migraine headache. Tearing of the layers of the carotid artery wall (carotid artery dissection) can also lead to Horner syndrome. Some individuals with congenital Horner syndrome have a lack of development (agenesis) of the carotid artery. Horner syndrome can also be caused by problems with the artery that supplies blood to the head and neck (the carotid artery ) on the affected side, resulting in loss of blood flow to the nerves. The nerves related to Horner syndrome can also be damaged by a benign or cancerous tumor, for example a childhood cancer of the nerve tissues called a neuroblastoma. Horner syndrome that occurs very early in life can lead to iris heterochromia because the development of the pigmentation (coloring) of the iris is under the control of the cervical sympathetic nerves.ĭamage to the cervical sympathetic nerves can be caused by a direct injury to the nerves themselves, which can result from trauma that might occur during a difficult birth, surgery, or accidental injury. Problems with the function of these nerves cause the signs and symptoms of Horner syndrome. The cervical sympathetic nerves control several functions in the eye and face such as dilation of the pupil and sweating. Within the autonomic nervous system, the nerves are part of a subdivision called the sympathetic nervous system. These nerves belong to the part of the nervous system that controls involuntary functions (the autonomic nervous system). Horner syndrome that appears after the newborn period (acquired Horner syndrome) and most cases of congenital Horner syndrome result from damage to nerves called the cervical sympathetics. However, the nerve damage that causes Horner syndrome may result from other health problems, some of which can be life-threatening.Īlthough congenital Horner syndrome can be passed down in families, no associated genes have been identified. The abnormalities in the eye area related to Horner syndrome do not generally affect vision or health. Individuals who develop Horner syndrome after age 2 do not generally have iris heterochromia. In people with Horner syndrome that occurs before the age of 2, the colored part (iris) of the eyes may differ in color (iris heterochromia), with the iris of the affected eye being lighter in color than that of the unaffected eye. Sinking of the eye into its cavity (enophthalmos) and a bloodshot eye often occur in this disorder. Horner syndrome is characterized by drooping of the upper eyelid ( ptosis ) on the affected side, a constricted pupil in the affected eye (miosis) resulting in unequal pupil size (anisocoria), and absent sweating (anhidrosis) on the affected side of the face. Horner syndrome can appear at any time of life in about 5 percent of affected individuals, the disorder is present from birth (congenital). Horner syndrome is a disorder that affects the eye and surrounding tissues on one side of the face and results from paralysis of certain nerves.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
